|
|
|

DROPimage
Standard
DROPimage Standard
ships with the Standard Goniometer (Model
200) and the
Contact Angle Goniometer with Wafer Support (Model
400).
It is
also available as an upgrade for users of DROPimage CA. DROPimage Standard is well suited for
contact angle and surface energy studies.
Below is
a link to a playlist of videos that illustrates how easy it is to calibrate the instrument and
take contact angle measurements using DROPimage
Standard.

Click here to watch DROPimage Standard Videos
This second-generation application
includes the following contact angle and surface energy tools:
|

|
Contact
Angle Tool |
|
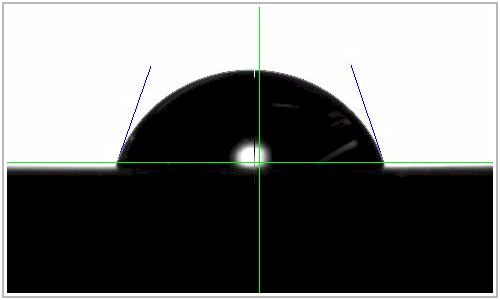
The
Contact Angle Tool characterizes the behavior of a liquid on a
solid. When a liquid is placed in contact with a solid surface, the
bare surface of the solid absorbs the vapor of the liquid until the
volatility of the absorbed material is equal to that of the liquid.
When equilibrium is established, there is a liquid-solid interface
between the two phases. The tangent angle between solid and liquid
is known as the contact angle. |
|

|
Acid-Base
Tool |
|
The
Acid-Base Tool evaluates the surface energy parameters of a given
solid using the contact angles of three different test liquids. Van
Oss, et al, have shown that the contribution due to acid-base
interactions can be expressed in terms of the product of their
electron donor and electron acceptor components by using three
liquids, one apolar and two polar. Recommended test liquids are methylene iodide or bromonaphthalene for the apolar liquid and a
polar liquid pair of either water and glycerol or water and
formamide.
To see this tool in action, watch this video:
http://youtu.be/VlbI7bUBuIk
References:
C.J. van Oss, R.J. Good and M.K. Chaudhury; Adv. Colloid Interface
Sci. 28, 35 (1987).
C.J. van Oss, R.J. Good and M.K. Chaudhury, J.; Chromatography 191,
53 (1987).
C.J. van Oss, R.J. Good and M.K. Chaudhury, J.; Langmuir 4, 884
(1988). |
|

|
Surface
Energy Tool |
|
The
Surface Energy Tool evaluates the surface energy of a given solid
using the contact angles of different test liquids.
The
geometric-mean method uses two pure liquids denoting their
dispersive and non-dispersive values. Water and methylene iodide are
a convenient choice for test liquids. Different liquid pairs tend to
give different results. The surface energies and polarities of some
low-energy solids obtained by this method are often much lower than
those calculated by other methods.
Reference:
D.K. Owens and R.C. Wendt, J Appl Polym. Sci. 13, 1741 (1969).
The
harmonic-mean method also uses two liquids in its calculations. The
results obtained with this method are regarded as accurate by Wu and
agree remarkably well with other methods. However, some researchers
consider that non-dispersive interactions across interfaces are
mainly of acid-base nature and in that situation recommend using the
acid/base tool.
Reference:
S. Wu, J Polym. Sci C34, 19 (1971).
In this video
http://youtu.be/5MGTb1EDSgE the contact angle of water is measured on
a sample of treated followed by diodomethane on the same sample. The
Surface Energy Tool is then used to calculate the surface energy.
|
|

|
Work
of Adhesion |
|
The
Work of Adhesion Tool determines an index of wetting ability of a
liquid for a solid. The Adsorption Theory proposes that van der
Waals interactions should be sufficient for good adhesion. The
liquid/solid thermodynamic considerations give rise to this equation
relating the reversible work of adhesion and surface free energies
according to Young and Dupre, noting that the process of adhesion
may be described in terms of opposites, namely the process of
separation.
Reference:
Buff, F.P. "The theory of capillarity", in Encyclopedia of
Physics; Flugge, S., Ed: Springer-Verlag: Berlin, 1960; pp. 281-304. |
|

|
Zisman's
Plot Tool |
|
The
Zisman’s Plot Tool summarizes wetting behavior and allows
predictions of an interpolative nature using a homologous series of
liquids. Extensive series of measurements of contact angles of
various liquids on low-energy polymer substrates were reported by
W.A. Zisman, inventor of the Ramé-Hart Contact Angle Goniometer,
and his coworkers at the Naval Research Laboratory. An empirical
linear relation was found between the cosine of the contact angle
and the surface tension of the liquid of the sessile drop. The
extrapolation of the line to cosine (theta) = 1 gives the
"critical surface tension" of the substrate.
The
term "critical" is used because any liquid on the Zisman
plot whose surface tension is greater than the "critical
surface tension" makes a finite contact angle with the
substrate. Critical surface tension values are useful empirical
values that characterize relative degrees of surface energy of
polymer substrates. Zisman’s empirical prediction fails for
liquids that form hydrogen bonds or acid-base interactions with the
substrate. These liquids would spread spontaneously on the
substrate.
Reference:
W.A. Zisman, ACS Adv. Chem. Ser. 43, 1 (1964). |
|
|
Solid-Liquid-Liquid
Surface Energy Tool |
|
The
Solid-Liquid-Liquid Surface Energy Tool evaluates the surface energy of a given solid using the contact angles of one test liquid on a solid submerged in a series of different liquids according to the method of Shultz et al.Water or formamide is usually used as the test liquid and a series of hydrocarbons as the continuos phase (hexane, cycohexane, octane, decane, hexadecane). At least 2 different
continuous phase liquids must be used. The method is especially useful for high-energy solids
such as metals and oxides that are otherwise wetted by most liquids.
Reference:
J.Schultz, K.Tsutsumi and J.-B. Donnet, J.Colloid Interface Sci 59, 272 and 277 (1977) |

|
|
Calibration
Command |
|
When
the instrument is shipped, the system is fully calibrated. However,
if the lens assembly is readjusted to any degree or any change is
made to the magnification system, the instrument is no longer
calibrated. The Calibration command uses a ball with a precise
diameter to calibrate the magnification of the camera, resulting in
100% accurate readings. The calibration can then be verified at any
time using a calibration check utility. All ramé-hart systems ship
with a proprietary floating calibration ball. |
|

|
Syringe
Tool |
|
The
Automated Syringe Tool supports the ramé-hart
Automated
Dispensing System option for the control of the drop volume. This
tool can be programmed into a time table for automated advancing and
receding and other types of studies. There is no limit to the number
of different timed measurements that can be programmed. |
|
